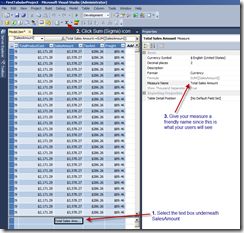
Learning to write MDX is difficult enough, but learning to write efficient MDX and performance tune an MDX query can be even more of a challenge. With that thought, I wanted to put together a few tips that can help you improve the performance of your MDX calculations.
1. Subdivide your calculations
For example, imagine you have an MDX query that looks like this one found in the AW cube:
Create Member CurrentCube.[Scenario].[Scenario].[Budget Variance]
As Case
When IsEmpty
(
(
[Measures].[Amount],
[Scenario].[Scenario].[Budget]
)
)
Then Null
When [Account].[Accounts].CurrentMember.Properties(“Account Type”) = “Expenditures”
Or
[Account].[Accounts].CurrentMember.Properties(“Account Type”) = “Liabilities”
Then ( [Measures].[Amount],[Scenario].[Scenario].[Budget] )
–
( [Measures].[Amount],[Scenario].[Scenario].[Actual] )
Else ( [Measures].[Amount],[Scenario].[Scenario].[Actual] )
–
( [Measures].[Amount],[Scenario].[Scenario].[Budget] )
End,
Format_String = “Currency”
You’ll notice the expressions ([Measures].[Amount],[Scenario].[Scenario].[Budget]), as well as ([Measures].[Amount],[Scenario].[Scenario].[Actual]), appear multiple times in the above calculation. Because a part of a calculation cannot be cached, each time this expression appears in the calculation, it has to be recalculated. We can subdivide this calculation into multiple calculations that can be individually cached the first time they are run.
Create Member CurrentCube.[Scenario].[Scenario].[Budget Amount] as
( [Measures].[Amount],[Scenario].[Scenario].[Budget] );
Create Member CurrentCube.[Scenario].[Scenario].[Actual Amount] as
( [Measures].[Amount],[Scenario].[Scenario].[Actual] );
Create Member CurrentCube.[Scenario].[Scenario].[Budget Variance]
As Case
When IsEmpty
(
[Scenario].[Scenario].[Budget Amount]
)
Then Null
When [Account].[Accounts].CurrentMember.Properties(“Account Type”) = “Expenditures”
Or
[Account].[Accounts].CurrentMember.Properties(“Account Type”) = “Liabilities”
Then [Scenario].[Scenario].[Budget Amount]
–
[Scenario].[Scenario].[Actual Amount]
Else [Scenario].[Scenario].[Actual Amount]
–
[Scenario].[Scenario].[Budget Amount]
End,
Format_String = “Currency”;
Now after the first time the measures Budget Amount and Actual Amount are calculated, they can be cached instead of having to be recalculated all over again.
2. Replace IIF functions with MDX scripting
If your calculation uses an IIF function to test for a specific location in the cube space, chances are it can replaced with better performing MDX scripting. Examples:
a. If the Current Member is in a specific level
b. If the Current Member is a certain member
c. If the Current Member has a certain parent
Here we have a calculation from the Adventure Works cube:
CREATE
MEMBER CurrentCube.[Measures].[Ratio to Parent Product] AS
IIF(
[Product].[Product Categories].CurrentMember.Level.Ordinal = 0
,1
,[Measures].[Sales Amount]
/
(
[Product].[Product Categories].CurrentMember.Parent
,[Measures].[Sales Amount]
))
,Format_String = “Percent”
,Associated_Measure_Group = ‘Sales Summary’ ;
The IIF function is testing for the very top level of the hierarchy. We can rewrite this query to eliminate the IIF function:
CREATE
MEMBER CurrentCube.[Measures].[Ratio to Parent Product] AS
[Measures].[Sales Amount]
/
(
[Product].[Product Categories].CurrentMember.Parent
,[Measures].[Sales Amount]
)
,Format_String = “Percent”
,Associated_Measure_Group = ‘Sales Summary’ ;
SCOPE ([Measures].[Ratio to Parent Product],[Product].[Product Categories]);
THIS=1;
FORMAT_STRING(THIS)=”Percent”;
END SCOPE;
By using the SCOPE statement, we can still set the top level of the of the Product Categories hierarchy to 1 and eliminate the IIF statement.
3. Don’t use Set Aliases in your calculations
Set Aliases are when you assign a set a name by creating a named set. Named sets are handy when you must define a set multiple times. But there’s a catch when using named sets: Using a named set in a calculation disables block computation. So take this query for example:
with set [SE States] AS
{[Geography].[State-Province].&[FL]&[US],
[Geography].[State-Province].&[GA]&[US],
[Geography].[State-Province].&[SC]&[US],
[Geography].[State-Province].&[TN]&[US]}
member [Measures].[SE States Sales] as
SUM([SE States],[Measures].[Reseller Sales Amount]),
format_string=”currency”
Select [Measures].[SE States Sales] on 0,
[Date].[Calendar Year].Members on 1
From [Adventure Works]
This calculation is calculated cell by cell because of the named set. If you “Analyze” this query in Mosha’s tool, MDXStudio (which is awesome and you should download now), you will see the warning, “Applying aggregation function Sum over named set [SE States] – this disables block computation mode.” Because its always possible to remove a named set, we should rewrite this query to use block computation:
with member [Measures].[SE States Sales] as
SUM({[Geography].[State-Province].&[FL]&[US],
[Geography].[State-Province].&[GA]&[US],
[Geography].[State-Province].&[SC]&[US],
[Geography].[State-Province].&[TN]&[US]},[Measures].[Reseller Sales Amount]),
format_string=”currency”
Select [Measures].[SE States Sales] on 0,
[Date].[Calendar Year].Members on 1
From [Adventure Works]
I hope you found this few simple tips useful. These tips are simple and easy to implement but can save you tons of query time.